January 8, 2026 by Yotta Labs
NVIDIA RTX 5090 Cloud GPU: Specs, Pricing, and Best Use Cases (2026)
The NVIDIA RTX 5090 has emerged as a surprisingly strong cloud GPU option for AI developers in 2026. With 32GB of GDDR7 VRAM and ~1.79 TB/s memory bandwidth, it lands in a “sweet spot” for teams running cost-sensitive LLM inference, image generation, and iterative workloads. But raw specs don’t tell the full story—what matters is how the 5090 compares to RTX 4090 and H100 in real deployment scenarios.
The NVIDIA GeForce RTX 5090 has become a surprisingly strong cloud GPU option for AI developers in 2026—especially for LLM inference, image/video generation, and fast iteration workloads where price-per-performance matters more than NVLink-scale training. With 32GB GDDR7, 21,760 CUDA cores, and ~1.792 TB/s memory bandwidth, the RTX 5090 often lands in a "sweet spot" for teams that need real throughput without paying H100/H200 pricing.
Why AI Developers Care About RTX 5090 in the Cloud
Most developers don’t choose a GPU because of peak TFLOPS—they choose it because:
- Does my model fit? (VRAM + KV cache headroom)
- How many tokens/sec do I get at my latency target?
- What’s the real $/token or $/image?
- Can I scale quickly without overcommitting budget?
The RTX 5090’s cloud appeal comes from two things:
- High bandwidth GDDR7 (unusually important for inference and diffusion-style workloads), and
- Much lower hourly pricing than datacenter GPUs in many markets ($0.65 vs. $2.45+ per GPU per hour).
RTX 5090 Key Specs (What Actually Matters for AI)
Here are the specs that show up in real AI workloads:
Core hardware specs
- VRAM: 32GB GDDR7
- Memory bandwidth: 1,792 GB/s (1.792 TB/s)
- Memory bus: 512-bit
- CUDA cores: 21,760
- AI TOPS: 3,352 TOPS (NVIDIA’s marketing metric)
- Interface: PCIe Gen 5
NVIDIA also notes RTX 5090 ships with 28 Gbps GDDR7 and 1.792 TB/s peak bandwidth, that probably explains why it performs well in bandwidth-sensitive inference.
Power (cloud-relevant, ops-relevant)
- NVIDIA’s system guidance references 850W minimum PSU for Founders Edition setups (for cloud operators, this translates to higher power density planning).
- Reviews commonly cite ~575W TGP for Founders Edition.
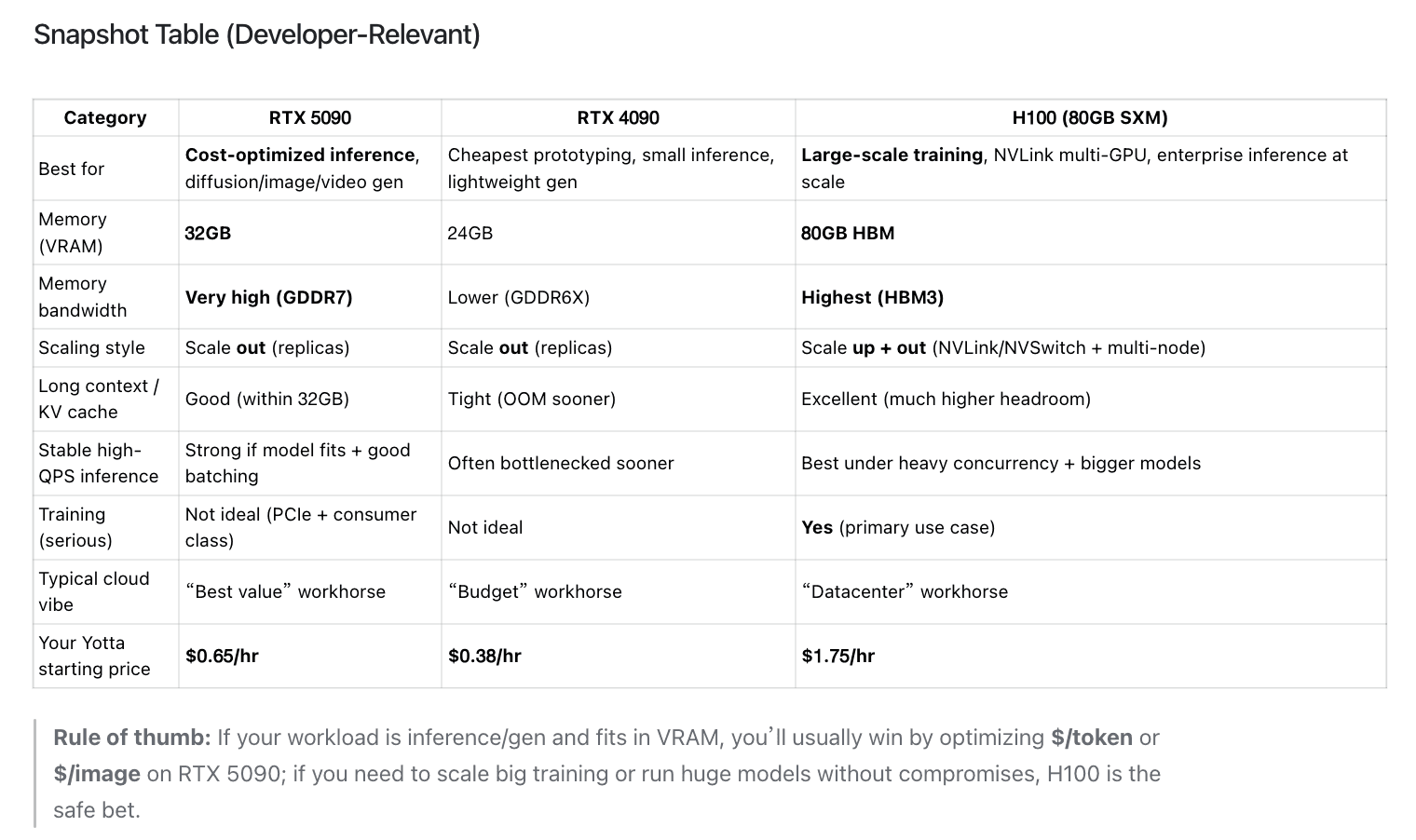
RTX 5090 vs RTX 4090 vs H100 — Quick Pick
Choose in 10 seconds
- Pick RTX 5090 if you want the best $ per output for inference + image/video gen, and your workload fits ≤32GB VRAM (or can be quantized).
- Pick RTX 4090 if you want the cheapest option for prototyping and you’re okay with lower bandwidth and smaller VRAM.
- Pick H100 if you need datacenter-grade training/inference, NVLink interconnection, and consistent performance at large scale.
"Can it run my model?" (Practical Fit Guide)
RTX 4090 (24GB):
- Great for smaller LLMs, lightweight quantized inference, and basic diffusion.
- Hits KV-cache/VRAM limits quickly with long context.
RTX 5090 (32GB):
- Much more comfortable for 32B-class quantized inference, higher-res diffusion, bigger ComfyUI graphs, and higher batch.
- Often the best "single-GPU cloud" value in 2026.
H100 (80GB):
- The "no-drama" option for long context, larger models, heavy concurrency, and training.
- Costs more per hour, but can win on $/token if it eliminates sharding/replicas or unlocks higher utilization.
RTX 5090 vs RTX 4090 vs H100: Where It Sits
RTX 5090 vs RTX 4090 (cloud buyer's view)
The 5090 is not just "a bit faster"—the big architectural uplift for AI workflows is memory bandwidth (GDDR7 + wider bus). Review coverage highlights 1,792 GB/s, described as a large jump over 4090-class bandwidth. What you feel in practice:
- better throughput on memory-touchy kernels
- more stable performance under concurrency
- fewer "it’s not compute-bound, it’s feeding the GPU" bottlenecks
RTX 5090 vs H100/H200 (the honest truth)
H100/H200 still dominate when you need:
- NVLink/NVSwitch fabric interconnectionscaling
- large multi-node training
- enterprise reliability + long-term cluster consistency
But for single-node inference and cost-sensitive production endpoints, the 5090 can be the better economic choice simply because of hourly pricing and availability.
Pricing: What "Good Value" Looks Like in 2026
MSRP (baseline reference)
NVIDIA lists RTX 5090 "Starting at $1999" (consumer channel) but you can rarely buy any if with less than $3000.
Cloud pricing (what developers actually pay)
In practice, what matters is $/hour → $/useful output:
- On Yotta Platform, you can rent RTX 5090 starting at $0.65/hr (US regions).
- That's meaningfully below H100/H200 class pricing and directly changes which workloads are economical to run continuously.
Developer rule: If 5090 achieves even “close enough” throughput for your workload, the cost curve often favors it—especially when optimizing for $/token.
Best Use Cases for RTX 5090 Cloud GPUs
This is the section that should drive conversions—because it maps directly to what developers are trying to run.
- LLM Inference for Small-to-Mid Models (and Quantized Larger Models)
RTX 5090 is strongest when:
- model weights fit comfortably in 32GB (or fit via quantization)
- your workload is throughput-per-dollar driven
- you want to scale replicas cheaply rather than scale one giant NVLink box
Common patterns:
- 7B–32B class models (especially quantized)
- Batch processing where throughput is more important than minimized latency
- RAG pipelines where retrieval dominates and model compute is moderate
Why it works: bandwidth helps, and the cost curve is usually attractive.
- High-Volume Image Generation (Stable Diffusion / Flux / ComfyUI)
For diffusion pipelines, you often pay for:
- memory bandwidth
- VRAM headroom (higher res, larger batch, more complex graphs)
- fast iteration loops
RTX 5090’s 1.792 TB/s bandwidth and 32GB VRAM are both directly relevant. If your product is "generate 1,000 images", you’ll often find the 5090 gives you a strong $ per image.
- Video Generation and Upscaling Pipelines
Video workflows (diffusion video, frame interpolation, upscalers) tend to be:
- VRAM hungry
- bandwidth hungry
- bursty (perfect for cloud)
5090 is a natural fit when you want a "creator GPU" but deployed as elastic infrastructure.
- Fine-tuning (LoRA / QLoRA) and Experimentation
For many teams, the real bottleneck is iteration speed:
- try a dataset tweak
- rerun a short fine-tune
- validate quickly
RTX 5090 is not "the best training GPU"—but it can be the best iteration GPU when you’re cost constrained and your fine-tune fits.
- Multi-Replica Inference (Scaling by count, not by NVLink)
If your service is latency-sensitive and you’d rather scale horizontally:
- 5090 often wins because you can run more replicas per budget
- elastic scaling makes more sense for real traffic patterns
When RTX 5090 Is Not the Right Choice
Be explicit here—this improves trust and keeps support tickets down.
Avoid RTX 5090 if you need:
- NVLink-dependent multi-GPU training efficiency
- very large dense models without quantization/sharding
- strict enterprise hardware consistency across long periods (depends on provider)
- multi-node collective-heavy training runs (network is often the bottleneck)
If your workload requires "datacenter GPU semantics", H100/H200/B200 class infrastructure is usually the better fit.
A Practical “Should I Use RTX 5090?” Checklist
Use RTX 5090 cloud GPUs if most of these are true:
- ✅ Your model fits in 32GB VRAM (or fits with quantization)
- ✅ You care about $ per token / $ per image, not peak training FLOPS
- ✅ Your workload is inference-heavy or gen-heavy
- ✅ You want fast iteration, experimentation, and easy scaling
- ✅ You’re fine scaling out via replicas (not NVLink scaling)
FAQ
How much VRAM does RTX 5090 have?
32GB GDDR7.
What is RTX 5090 memory bandwidth?
1,792 GB/s (1.792 TB/s).
Is RTX 5090 good for LLM inference?
Yes—especially for cost-sensitive inference where models fit in VRAM (often via quantization), and for scaling via replicas rather than NVLink.
What is the RTX 5090 price?
NVIDIA lists it starting at $1999 MSRP (consumer reference point). But typically costs more than $3000.
Does RTX 5090 replace H100/H200?
Not for large-scale training or NVLink-heavy workloads. It’s a cost-optimized option for many inference + gen workloads.
Deploying RTX 5090 on Yotta
If you’re choosing a cloud GPU, don’t pick from spec sheets alone—benchmark with your own workload:
- vLLM / SGLang (tokens/sec under your real prompt distribution)
- ComfyUI graphs for your real resolutions and batch sizes
- measure $/token or $/image, not just $/hour
On Yotta, your published starting price for RTX 5090 is $0.65/hr (US regions), making it a strong default for cost-optimized inference and generation stacks.