February 6, 2026 by Yotta Labs
Orchestrating AI Across Multi-Silicon, Multi-Cloud, and Heterogeneous Clusters
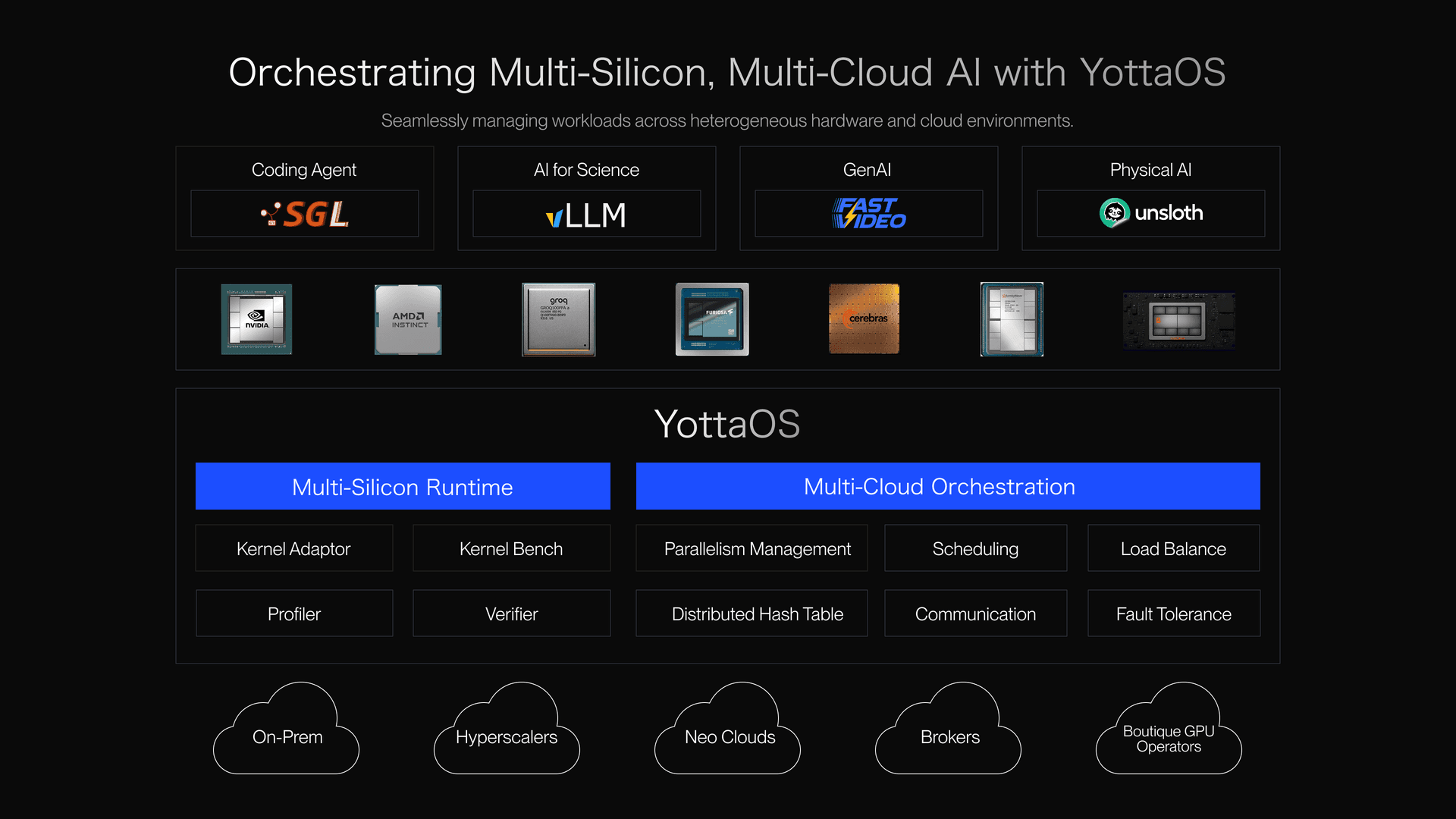
Modern AI workloads are no longer confined to a single GPU or cloud. Today’s models are trained and deployed across NVIDIA H100s, AMD MI300s, Google TPUs, AWS Trainium, and emerging accelerators, running across AWS, GCP, Azure, and private data centers. This heterogeneity offers unprecedented performance and cost efficiency potential—but it also introduces a new class of operational complexity that traditional cloud orchestration platforms were never designed to handle.. Without a unified systems layer, teams face fragmented tooling, inefficient utilization, and fragile production pipelines.
At Yotta Labs, we are solving the dual challenge of multi-silicon and multi-cloud orchestration. Our mission: to provide a unified AI operating system that abstracts hardware and cloud differences while maximizing efficiency, scalability, and reliability.
The New Reality: Heterogeneous AI at Scale
Distributing AI workloads across multi-silicon and multi-cloud environments presents several challenges:
- Diverse runtimes and APIs: Each accelerator has unique kernel implementations, memory hierarchies, and interconnects.
- Fragmented resources: Idle GPUs or underutilized cloud instances inflate costs.
- Non-portable optimizations: Operator fusion or kernel tuning optimized for one accelerator rarely works on another.
- Distributed synchronization overhead: Gradient updates, pipeline parallelism, and sharded datasets across clouds introduce latency and bandwidth constraints.
Without a unified orchestration layer, engineering teams spend more time managing infrastructure than improving models.
How Yotta Labs Orchestrates Multi-Silicon, Multi-Cloud Workloads
The Yotta Labs AI OS abstracts complexity while delivering peak performance. It provides cluster-level scheduling, device-aware memory management, and cross-cloud optimization—all through unified APIs.
Here’s how it works in practice:
1. Intelligent Workload Scheduling
Yotta continuously profiles workloads across:
- Compute intensity
- Memory requirements
- Communication patterns
- Network latency
Using this telemetry, the scheduler dynamically maps tasks to optimal devices and regions.
Example
A hybrid model with attention-heavy layers and large convolutional layers is split across NVIDIA H100s for matrix-heavy operations and AMD MI300s for tensor-intensive operations, maximizing throughput.
The scheduler continuously monitors GPU utilization and latency, moving tasks between devices and clouds to avoid bottlenecks.
Key capabilities:
- Hardware-aware placement
- Cross-region load balancing
- Utilization-driven reallocation
2. Memory-Aware Optimization
Memory fragmentation and limited GPU RAM are major constraints for large-scale models. Yotta implements device-aware memory management:
- Hierarchical allocation
- Dynamic tensor placement
- Intelligent offloading
- Cross-device memory pooling
Example
During multi-cloud distributed training, embeddings and intermediate tensors are offloaded to high-bandwidth caching nodes when local GPU memory approaches saturation, reducing out-of-memory errors.
Operator fusion and memory reuse strategies ensure that each accelerator runs at maximum memory efficiency, even when executing heterogeneous workloads.
3. Throughput Balancing Across Clusters
Throughput is maximized by balancing workloads across GPUs, accelerators, and clouds. Yotta optimize batch sizes, pipeline depth, device assignments, and communication topology to maintain global optimal performance
Example
A hybrid inference workload spreads requests across GCP TPUs and AWS H100 nodes. Latency-sensitive requests are routed to low-latency regions, while batch-processing jobs utilize idle capacity in lower-cost clouds.The system automatically adjusts batch sizes, device assignments, and communication patterns to maintain steady throughput without overloading any single resource.
4. Cross-Cloud Synchronization and Reliability
Distributed AI systems must tolerate partial failures, network variance, and cloud outages. The OS manages gradient synchronization, pipeline parallelism, and checkpointing across clouds with minimal latency impact
- Gradients are compressed and asynchronously synchronized across regions to reduce network overhead.
- Checkpoints are stored redundantly in cloud-agnostic storage to ensure resiliency against outages.
This enables faster recovery, reduced training disruption, and predictable production behavior.
What This Enables for AI Teams: Seamless Multi-Silicon, Multi-Cloud AI
With Yotta Labs, AI teams gain system-level leverage. They can:
- Train and deploy models that span GPUs, TPUs, and emerging accelerators without rewriting code.
- Optimize memory usage dynamically, scaling model size without increasing cost.
- Balance workloads across clouds and accelerators for maximum performance and efficiency.
- Adopt new hardware or cloud platforms immediately, without manual profiling and retuning
From Infrastructure Management to Model Innovation
The next decade of AI will be defined by:
- Heterogeneous accelerators
- Distributed execution
- Elastic scheduling
- Continuous hardware evolution
Winning teams will not be those with the most GPUs—but those with the most efficient orchestration layer for multi-silicon, multi-cloud workloads.
Yotta Labs is building that layer.
By abstracting hardware complexity and embedding optimization into the control plane, we make infrastructure invisible, so teams can focus on building models, products, and breakthroughs.
The future of AI is heterogeneous, distributed, and dynamic. Yotta makes it operable.